

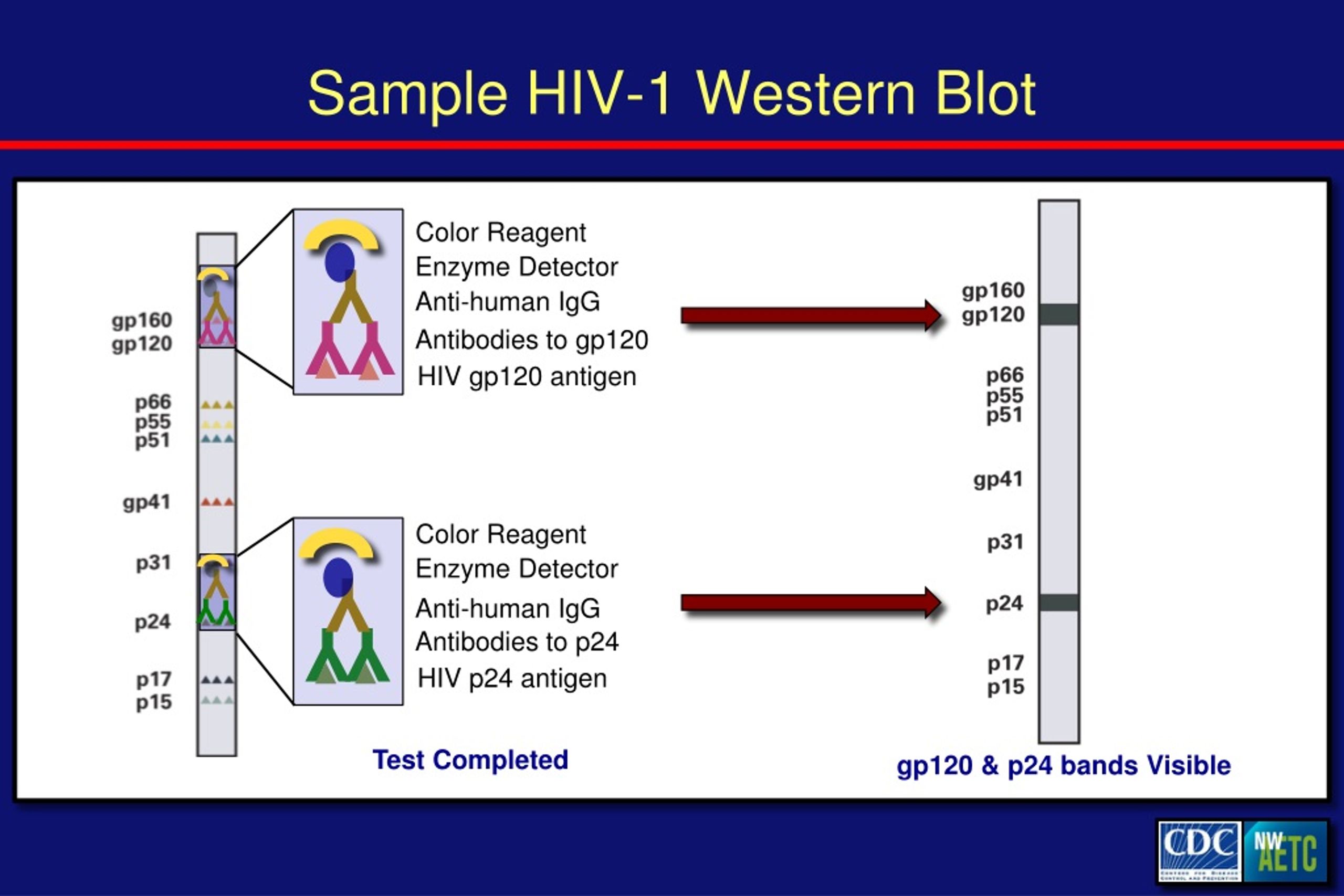
Sometimes, HIV doesn’t show up on the ELISA test even though a person has an HIV infection. If the person tests positive for HIV with either one of these tests, they probably have HIV. These tests include the differentiation assay and a test called the nucleic acid test (NAT). For example, having certain conditions such as Lyme disease, syphilis, or lupus may produce a false positive for HIV in an ELISA test.įor this reason, after a positive ELISA test, more sophisticated tests are done to confirm whether the person has HIV. This means that test results indicate that the person has HIV when they actually do not. However, there can be false positives with the ELISA test. If a person tests positive for HIV on the ELISA test, they might have HIV. The specific antibodies and antigens in the blood are separated and identified in a different immunoassay device. The differentiation assay is very similar, but instead of an automated machine, the device can be handled by a lab technician. If this binding is detected, the person may have HIV. If the blood contains antibodies to HIV or antigens of HIV, it will bind with the antigen or antibody in the device. Afterward, the reaction of the blood and the antigen will be monitored. The enzyme helps speed up chemical reactions. A lab technician will add the sample to a device that contains HIV antigen and anti-HIV antibodies.Īn automated process will add an enzyme to the device. Testing the bloodįor the ELISA test, the blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis. Their arm may throb slightly after the procedure. Giving a blood sample isn’t painful, though the person may feel a sting or a pricking sensation as the needle goes into their vein.
To decrease further bleeding, after the test the person may be asked to elevate or flex their arm to reduce blood flow.
Western blot hiv test skin#
clean the skin site where they plan to draw blood.The procedure for getting a sample of blood is the same for both tests. they’re taking anticoagulant medications ( blood thinners).they have a bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia.they’ve had trouble giving blood in the past.To help prevent any problems during the test, the person should be sure to tell the healthcare provider if: The person having the test will probably need to sign a consent form. Before the test, a healthcare provider will explain the procedure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
